Cell cycle regulation YouTube Biology Diagrams We briefly discuss G1-S transcriptional regulation in the context of other cell cycle pathways, such as cyclins and CDKs, checkpoint signalling and the ubiquitin ligase regulatory pathways, but we also refer readers to more comprehensive reviews on these specific topics 17 - 22.

Learn about cell cycle checkpoints and their role in regulating the cell cycle. Specializing cells for specific functions. Regulation of the Cell Cycle Checkpoints tightly regulate the cell cycle to prevent errors. These checkpoints include: G1 Checkpoint: This checkpoint ensures that the cell has adequate energy resources and that the surrounding environment is favorable for DNA replication.

Cell Cycle Phases and Checkpoints Biology Diagrams
These checkpoints occur near the end of G 1, at the G 2 /M transition, and during metaphase. Figure 10.3B. 1 10.3 B. 1: Internal Checkpoints During the Cell Cycle: The cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. The integrity of the DNA is assessed at the G1 checkpoint. Proper chromosome duplication is assessed at the G2 checkpoint.
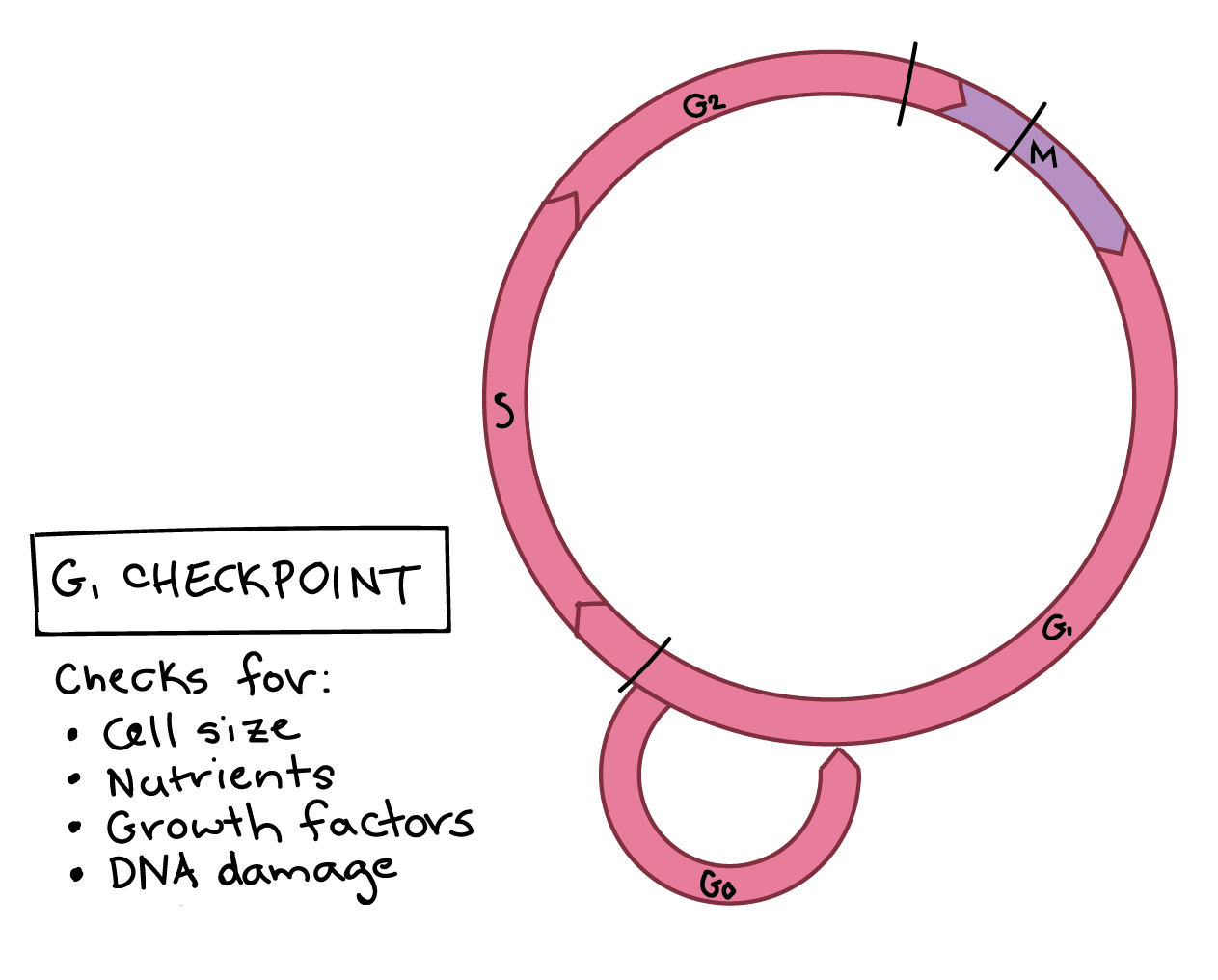
In Eukaryotic cells, cell cycle checkpoint regulation ensures the fidelity of cell division. This kind of control verifies whether the processes at each phase of the cell cycle have been accurately completed before progression into the next phase. Mitogen-dependent progression through the first gap phase (G1) of the mammalian cell-division cycle is precisely regulated so that normal cell

Cell Cycle: G1/S Checkpoint Regulation Biology Diagrams
The DNA damage checkpoint pathways consist of lesion sensors, adaptors/mediators that assemble signaling complexes at DNA lesions, protein kinases, and their substrate effectors (Table 1). The proteins identified as components of the DNA damage checkpoint pathways are part of the surveillance network that also regulates the orderly progression through an unperturbed cell cycle. Although the G1
